What is Empathy & Why Is It So Important?
July 6, 2025 | By Penelope Dean
Empathy is a term frequently used in conversations about relationships, personal growth, and even professional success, but what is empathy really, and how does empathy affect relationships and our daily lives? Many wonder about the true empathy definition and its significance beyond just being "nice." If you're curious to understand this fundamental human capacity and how it shapes our world, you've come to the right place. Understanding empathy can be the first step towards improving your emotional intelligence, and you can even explore your empathy profile with our free test.
Defining Empathy: Understanding Its Types and Crucial Role
At its heart, empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person. It's about stepping into their shoes and seeing the world, or a particular situation, from their perspective. This emotional understanding is more profound than simply acknowledging someone's situation; it involves a genuine attempt to connect with their emotional state. This ability is foundational to building meaningful connections and navigating complex social landscapes.

Unpacking "What is Empathy": Beyond Just Feeling Sorry
Often, people confuse empathy with sympathy or pity. While related, they are distinct. What is the main difference between empathy and sympathy? Sympathy involves feeling sorry for someone, creating a sense of distance, whereas empathy is about feeling with someone, fostering connection.
The Core Definition of Empathy: Stepping into Someone's Shoes
The core empathy definition centers on the capacity for perspective taking – imagining yourself in another's situation and attempting to understand their feelings, thoughts, and experiences as if they were your own. It's not about agreeing with them, but about understanding them. This skill is vital for effective communication and resolving conflicts constructively.
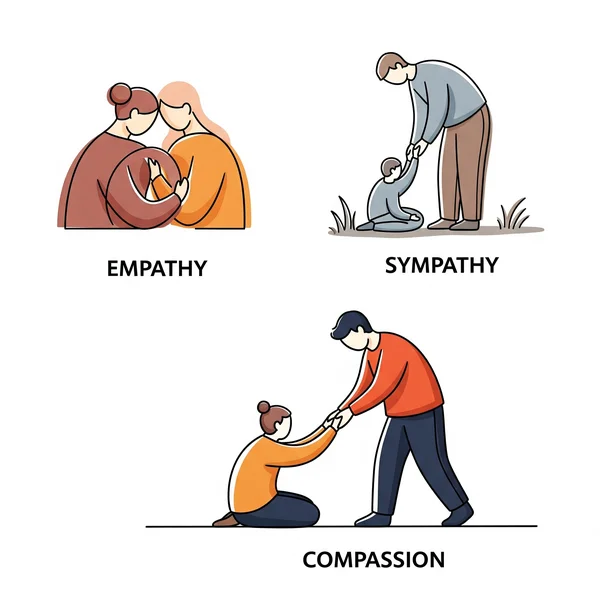
Empathy vs. Sympathy vs. Compassion: Clearing the Confusion
It's crucial to distinguish these terms for better emotional understanding.
- Empathy: Understanding and sharing another's feelings. For example, if a friend is sad about losing a pet, you try to feel that sadness with them.
- Sympathy: Feeling pity or sorrow for someone else's misfortune. You might say, "I'm so sorry for your loss," acknowledging their pain from an observer's standpoint.
- Compassion: This takes empathy a step further. It's not just about feeling with someone but also involves a desire to help alleviate their suffering. Compassionate empathy often translates into action.
Understanding these nuances helps us respond more appropriately and effectively in various social interactions.
Exploring the Different Types of Empathy
Empathy isn't a monolithic concept; it has different facets. Why is understanding different types of empathy useful? Recognizing these distinctions allows for a more nuanced appreciation of our emotional experiences and interactions. Researchers generally identify a few key types of empathy:
Affective Empathy: Feeling What Others Feel
Affective empathy, often called emotional empathy, is the ability to experience an appropriate emotional response to another person's emotional state. It's about mirroring or sharing their feelings – feeling distress when they are distressed, or joy when they are joyful. This type of empathy relies heavily on our capacity for shared feelings and emotional contagion. For instance, you might tear up watching a sad scene in a movie because you are experiencing affective empathy for the characters.
Cognitive Empathy: Understanding Others' Perspectives
Cognitive empathy is the intellectual ability to understand another person's mental state or to put yourself in their place and see things from their viewpoint. It’s about understanding what they might be thinking or feeling, without necessarily sharing the emotion itself. This form of perspective taking is crucial for effective communication, negotiation, and understanding motivations. For example, a manager using cognitive empathy can understand why an employee might be underperforming by considering their personal challenges.
Compassionate Empathy (Empathic Concern): The Drive to Help
Also known as empathic concern, compassionate empathy combines both affective and cognitive elements with an added motivation to care for the other person's well-being and a desire to help if needed. It moves beyond just understanding or feeling; it propels us to action. This is where empathy translates into supportive behavior and is a cornerstone of altruism and strong interpersonal skills.
The Profound Importance of Empathy in Our Lives
The importance of empathy cannot be overstated. It permeates every aspect of our existence, from our closest relationships to our broader societal interactions. How does empathy affect relationships? It's the glue that binds us.

Building Stronger Connections: Empathy in Personal Relationships
In personal relationships, empathy fosters trust, intimacy, and mutual understanding. When we feel understood and validated by our partners, friends, and family, our bonds deepen. It allows us to navigate disagreements more constructively and provide meaningful support. Strong healthy relationships are often built on a foundation of mutual empathy and emotional understanding.
Fostering Success: Empathy in the Workplace and Leadership
In the professional sphere, empathy is a key ingredient for team collaboration and effective communication. Empathetic leaders are better at understanding their team's needs, motivating them, and creating a positive work environment. This, in turn, can lead to increased productivity and employee loyalty. Many organizations now recognize the importance of empathy in customer service and building strong client relationships.
Enhancing Well-being: The Role of Empathy in Mental Health
Empathy also plays a significant role in our own mental health. Practicing empathy can enhance self-awareness and emotional regulation. By understanding others' emotions, we can often gain better insight into our own. Furthermore, experiencing empathy from others can be incredibly validating and reduce feelings of isolation. If you're curious about your own empathy levels and how they impact your well-being, you might consider taking an empathy test to learn more.
Embrace Empathy: A Key to a More Connected World
Understanding what is empathy and its various forms – affective empathy, cognitive empathy, and compassionate concern – reveals its profound impact. It's more than a soft skill; it's a fundamental human capacity that enriches our personal lives, strengthens our professional endeavors, and contributes to a more compassionate society. By cultivating empathy, we not only improve our interpersonal skills but also contribute to a more understanding and connected world.
Your Empathy Questions Answered
Here are some common questions about empathy:
-
What is the main difference between empathy and sympathy? Empathy is about feeling with someone by understanding their perspective and emotions, fostering connection. Sympathy is feeling for someone, often expressing sorrow or pity from a more detached standpoint. True emotional understanding comes from empathy.
-
Can empathy be learned or improved? Yes, absolutely! While some people may be naturally more empathetic, empathy is a skill that can be developed and strengthened through conscious effort, practice (like active listening and perspective taking), and self-reflection. Many find that understanding their baseline through an online empathy test is a helpful first step.
-
Is it possible to have too much empathy? While empathy is generally positive, an overabundance of affective empathy without sufficient emotional boundaries or emotional regulation skills can sometimes lead to empathic distress or burnout. It’s about finding a healthy balance.
-
Why is understanding different types of empathy useful? Recognizing the types of empathy (affective, cognitive, compassionate) helps us understand the multifaceted nature of this ability. It allows us to identify which aspects we might be stronger in or need to develop further, leading to more effective communication and richer healthy relationships.
We hope this exploration has clarified what is empathy and highlighted its incredible importance of empathy in our lives. If you're interested in a deeper dive into your own empathetic tendencies, consider exploring resources like the empathy test available on our site.